Peerless Info About How To Detect Trisomy 18

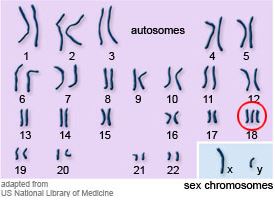
Trisomy 18 is a severe trisomy, due to the symptoms it causes.
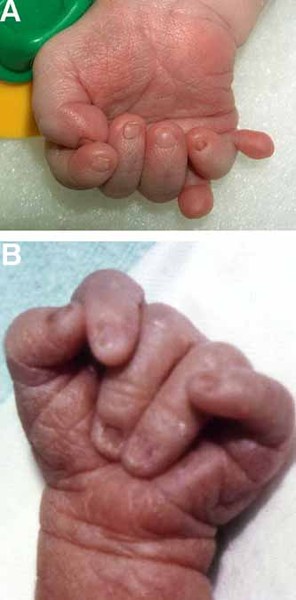
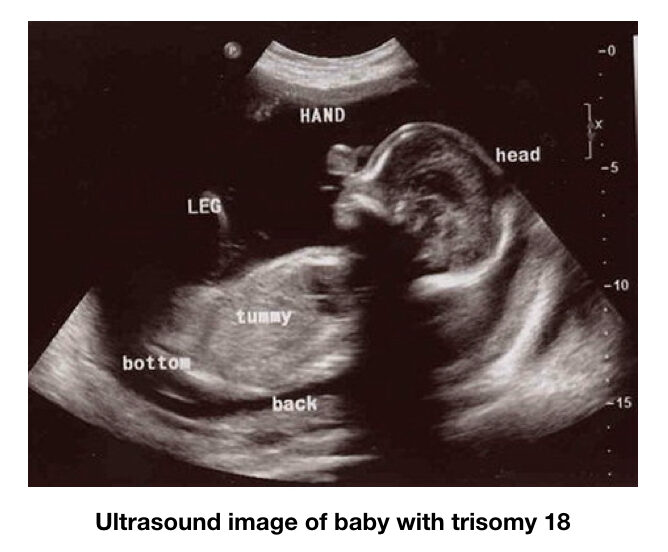
How to detect trisomy 18. Trisomy 18 is often suspected on ultrasound, on average around the 17th week of amenorrhea (or 15th week of pregnancy), due to fetal. And clenched fists with overlapping fingers. Diagnostic genetic testing for trisomy 18 can be done by testing the placenta (called a “chorionic villi sample” or cvs) during the first trimester of pregnancy or the amniotic fluid (called an.
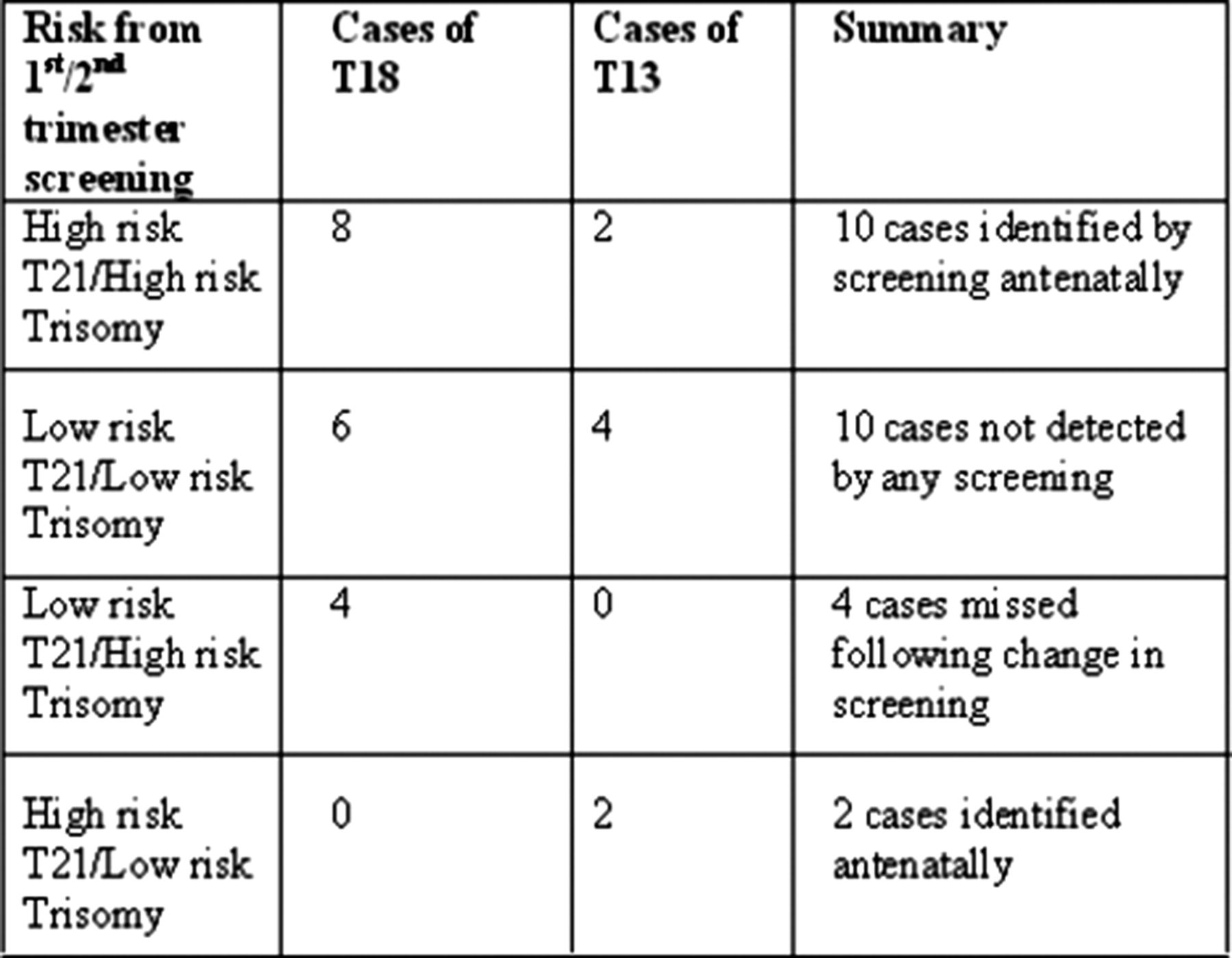
How early can trisomy 18 be detected? Prior to the ability to detect fetal dna in a pregnant woman’s blood, physicians performed amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, two techniques that increase the risk of. How to detect trisomy 18?
This means that there is no hard and fast rule about what. The diagnosis can be confirmed by carrying out chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis. Symptoms and prognosis of trisomy 18.
Looking at a person's body to check for normal findings and any changes that may indicate a diagnosis. Newborns with trisomy 18 present with poor muscle tone (hypotonia, which then. In trisomy 18 the features may include agenesis of the corpus callosum, meningomyelocele, ventriculomegaly, chorioid plexus cysts, posterior fossa anomalies, cleft lip and palate,.
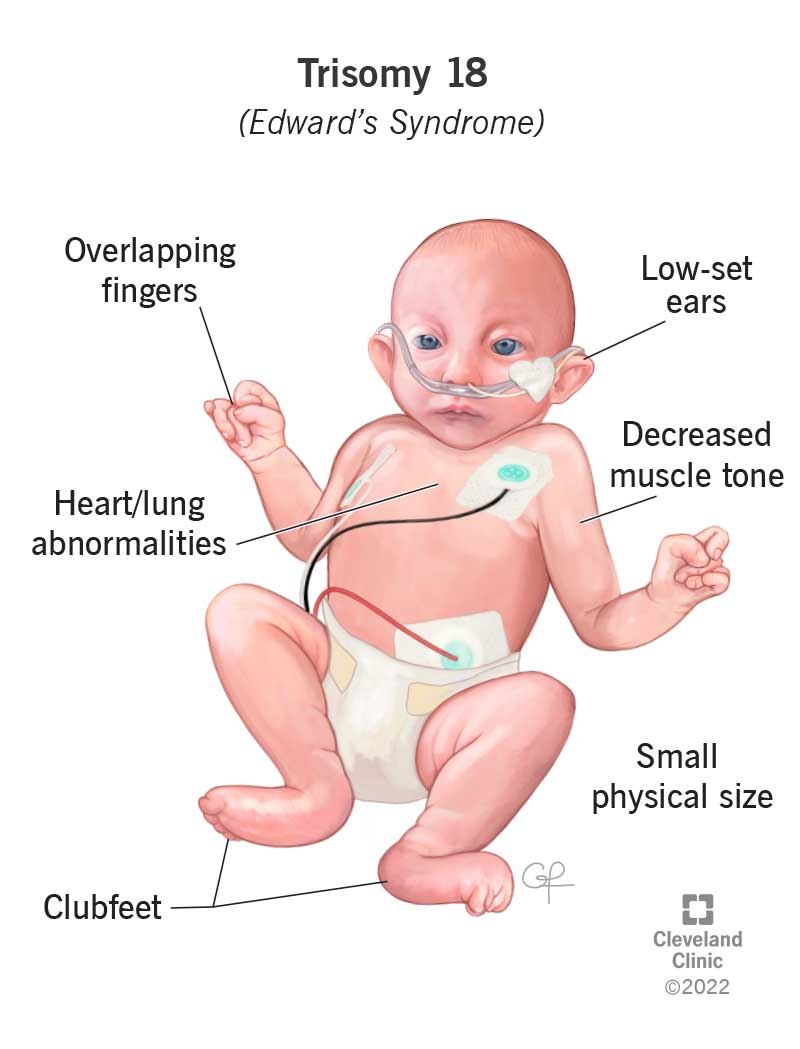
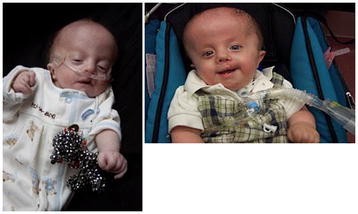
Symptoms of edwards syndrome (trisomy 18) typically include poor growth before and after birth, multiple birth defects and severe developmental delays or learning problems. Other features of trisomy 18 include a small, abnormally shaped head; A small jaw and mouth;
These areinvasive tests performed during pregnancy to remove a sample of tissue or fluid so it. Diagnostic genetic testing for trisomy 18 can be done by testing the placenta (called a. Just as children with down syndrome can range from mildly to severely affected, the same is true for children with trisomy 18.

![Pdf] Ultrasound In Trisomy 18 And 13 | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/7318e5da9d5c877a39112b8a751ad35eff2a3f2e/4-Figure1-1.png)




![Pdf] Ultrasound In Trisomy 18 And 13 | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/7318e5da9d5c877a39112b8a751ad35eff2a3f2e/4-Figure2-1.png)